Abstract
This horizontal evaluation uses Allsheng® and the mainstream FFPE tissue sample DNA extraction cartridges in domestic and international markets to make a detailed comparison of the extraction effect. The main indexes is nucleic acid extraction efficiency and fragment size and distribution, the former is quantified by Fluo-200 fluorometer, and the latter is detected by biological analyzer.
The results showed that the Allsheng cartridges performed consistently with other brand cartridges in terms of DNA extraction rate and product fragment distribution, and even outperformed similar products on some samples.
In addition, we compared the difference between Allsheng® FFPE tissue sample DNA extraction cartridges extraction by manual method and the automated extraction on the fully automated extraction on Leap-Pure S24.
The results showed that there was no significant difference in the yield of nucleic acids and fragment integrity obtained by the above two methods.
Reagent Introduction
FFPE (Formalin fixation and paraffin embedding), i.e. formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tissue samples, are regarded as the "jewels" of the Department of Pathology, because they preserve a large amount of disease-related information, provide a valuable source of data for medical research, and are the main method of long-term preservation of pathological samples, which has been used to archive a large number of biological samples around the world over the past few decades.
However, due to technological limitations, FFPE has not been fully utilized in the past decades. With the advancement of technology and the development of research, the application of FFPE has now become more and more widespread. From the initial use of immunohistochemistry for disease diagnosis and pathotyping, to the fact that it has now been applied to a variety of histological studies, the value of FFPE has been more fully explored.
Each FFPE is precious and unique. With a limited sample size, we should release the biological information contained in the sample while minimizing the loss. Extracting nucleic acids from FFPE samples is still challenging at this stage. For example, the degradation of nucleic acids during the production of paraffin samples makes it difficult to be compatible with downstream applications such as qPCR and sequencing, as well as the cumbersome and time-consuming extraction process, xylene in the reagents can be hazardous to the health of the experimenter, and secondly, xylene affects the quality of the tissue sections, and if it is not used appropriately, it is likely to cause the tissue to shrink, harden and become brittle, and other changes.
Therefore, we need to extract as much high-quality nucleic acid as possible from limited samples, and at the same time realize the automation of the extraction operation. Here we show the method of extracting genomic DNA from rat paraffin-embedded tissue samples and human tissue samples by Allsheng cartridges, and compare it with the extraction effect of the same type of kits in the market, and the results show that the DNA extraction concentration and completeness of DNA extraction are consistent with the performance of the same type of products at home and abroad.
Materials and Methods
Comparison of Reagent Extraction Efficiency
Three different batches of reagents were prepared, and according to the size of the tissue area of FFPE sections/rolls, 5-10 rolls with a surface area of 25-30 mm2 were scraped, respectively, extracted by manual method, and all samples were eluted in equal volume (50 μL) The extraction process was shown in Figure 1. The resulting purified DNA was accurately quantified for extraction concentration (dsDNA) by Fluo-200 Fluorometer dsDNA high sensitive quantification cartridge and DNA integrity was verified by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the DNA products were analyzed by qPCR using the GAPDH gene (amplicon lengths of 322bp and 99bp, respectively), with the same starting volume/volume for all samples.
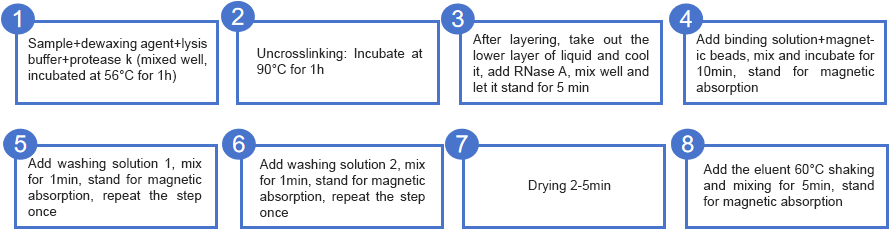
Figure 1 Overall Reagent Operation Flow
The above figure shows the operation flow of Allsheng cartridges. The manual extraction requires adding reagents in sequence according to the steps. With the automatic extraction method, you only need to add the sample directly into the designated wells, and the rest of the reagents are added to the other wells in advance, which is relatively more convenient.
Comparison of the Extraction Effect of Various Brands of Reagents
Allsheng cartridges and three other domestic and foreign referenced cartridges were used to extract FFPE from different human tissues, with equal volumes (50 μL) eluting all samples, passing the purified DNA through Fluo-200 fluorometer and dsDNA high-sensitivity quantification analysis cartridges for precise quantitative extraction concentration (dsDNA), agarose gel electrophoresis to verify DNA integrity, and with Allsheng® NGS Universal DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina cartridges were used to compare the library production and peak pattern analysis of different brands of extracted products. Comparison with similar products for extracting human paraffin embedded tissue samples.
Validation of Automated Extraction Effects
To determine whether fully automated and manual extraction methods can achieve the same nucleic acid yield and quality, we used the Allsheng cartridges for manual extraction and fully automated extraction of continuous FFPE on Leap-Pure S24. The sample size is consistent for each sample, and the elution volume is 50 μL for comparison testing.
Results and Analysis
Reagent Extraction Efficiency Validation
Analysis of the three batches of extracted product concentration analysis found that the extraction efficiency of Allsheng® and A brand cartridges for different FFPE tissue samples was close to or exceeded that of the standard reagent (Figure 2-1), the fragment distribution and fragment completeness (amplification of the product with primers of different sizes, and agarose gel electrophoresis of amplified products, which all showed four complete fragments) were consistent with that of the standard product (Figure 2-2, Figure 2-3), and the qPCR analysis of DNA products for GAPDH gene (amplified fragment length of 322bp and 99bp, respectively) found no significant difference in the concentration of amplified fragments of different lengths (Figure 2-4).
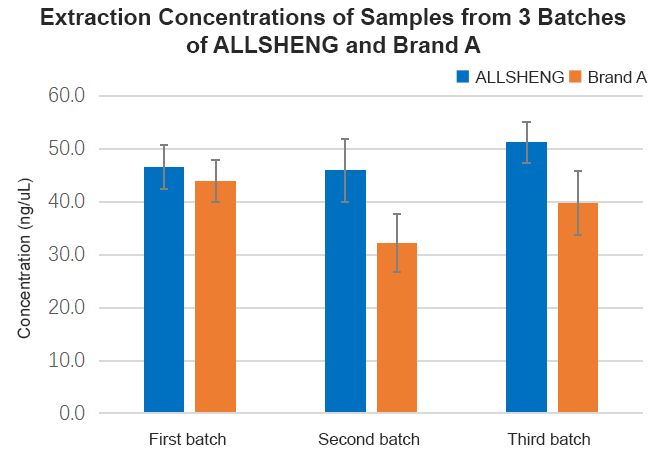
Figure 2-1 Allsheng® FFPE Tissue Sample DNA Extraction Cartridges and Reference Cartridges Extraction Product Concentration
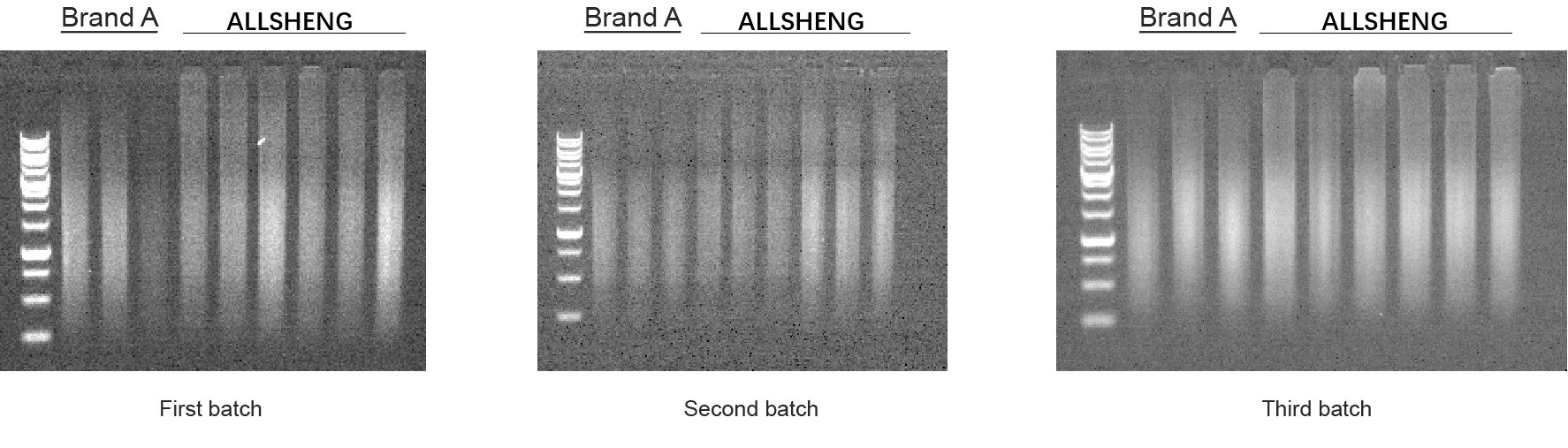
Figure 2-2 Allsheng® FFPE Tissue Sample DNA Extraction Cartridges and Reference Cartridges for Agarose Electrophoresis of Extracted Products
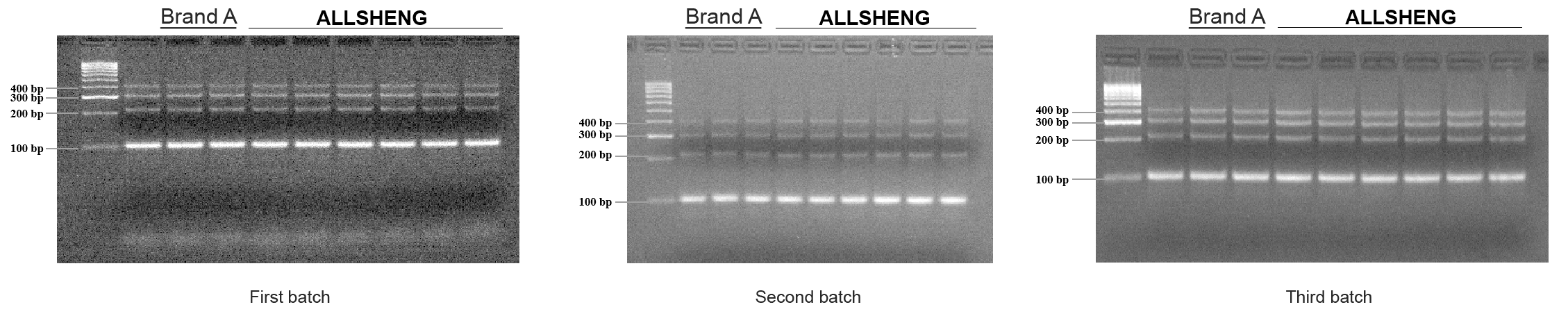
Figure 2-3 Allsheng® Fragment Integrity Analysis Results of FFPE Tissue Sample DNA Extraction Cartridges and Reference Cartridges Extraction Products
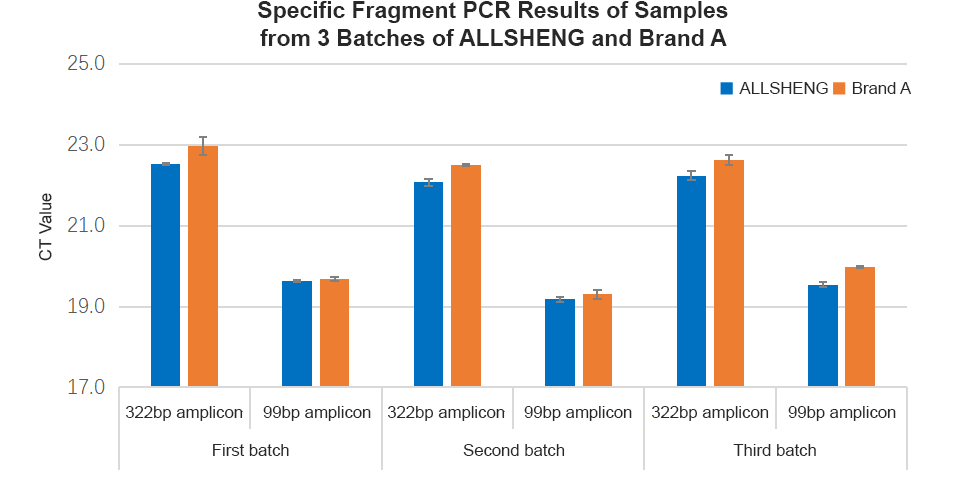
Figure 2-4 qPCR Results of Different Fragments of Extracted Products
Validation of Extraction Effects of Various Brands of Reagents
Through the FFPE extraction from different human organizations, it was found that the extraction performance of the four cartridges was consistent for different samples. The extraction efficiency of the Allsheng cartridges and three other domestic and foreign referenced cartridges varied for different samples. In the extraction of sample C, the extraction efficiency of the Allsheng cartridges was significantly higher than that of the three referenced cartridges (Figure 3-1), and the fragment distribution and integrity of the three samples were consistent with the referenced products (Figure 3-2). The same amount of extracted products from the four cartridges were used to the library preparation, and there was no significant difference in the library production after the Allsheng cartridges were built compared to the library production of the other three cartridges.
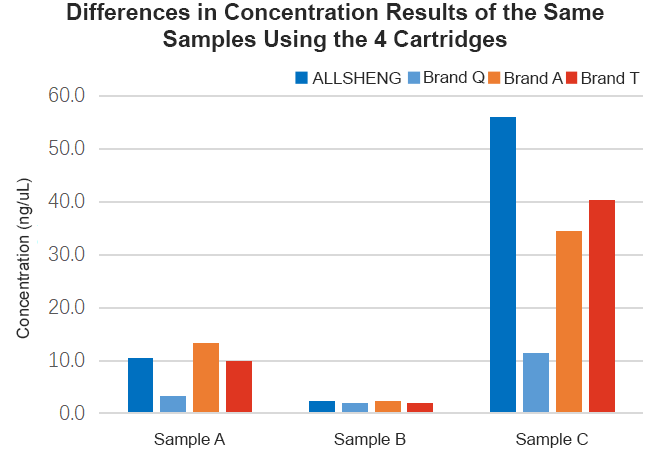
Figure 3-1 Concentration of FFPE Extracted from Different Human Tissues Using Four Different Cartridges
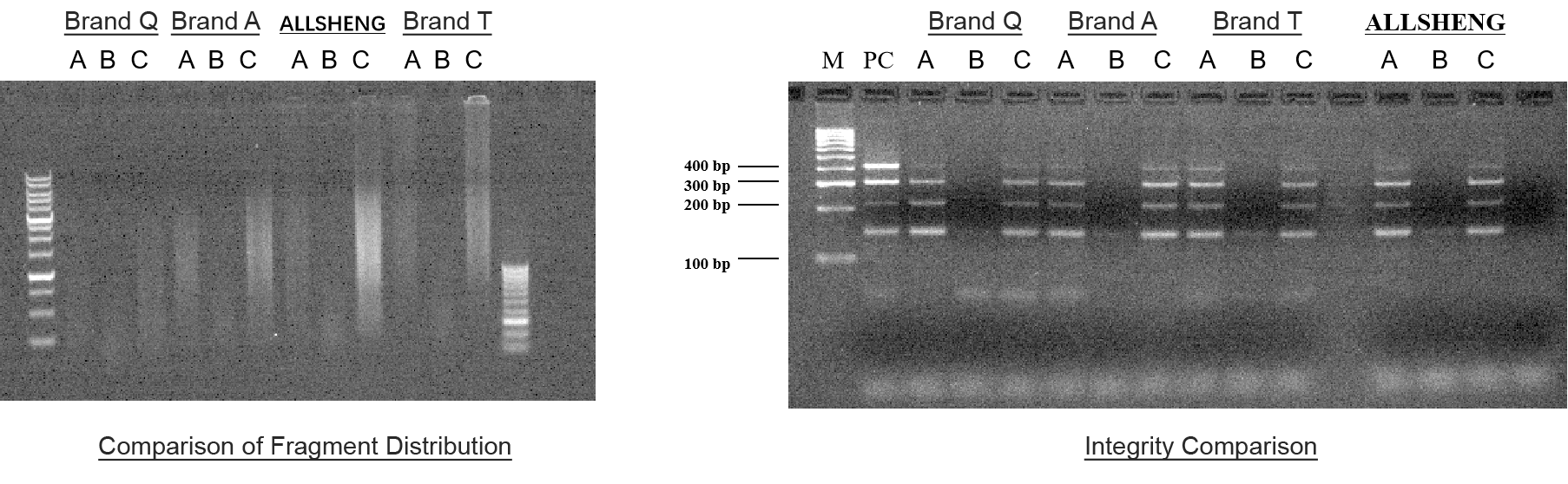
Figure 3-2 Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Diagram and Integrity Analysis Diagram of the Extracted Products of FFPE from Different Human Tissues Extracted by Four Cartridges
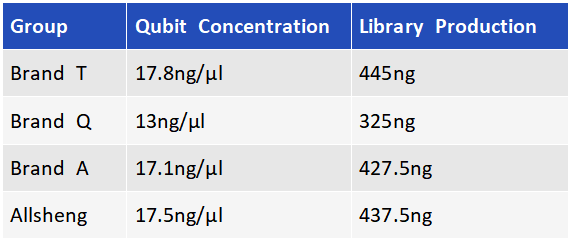
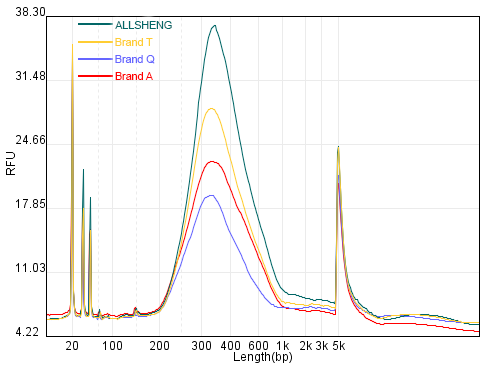
Figure 3-3 Results of Library Preparation Experiments of the Extracted Products of the Four Cartridges
Validation of Automated Extraction Effects
Comparison between fully automatic extraction on Leap-Pure S24 and manual extraction of continuous FFPE, the results show that the concentration of Leap-Pure S24 extract products can reach more than 90% of the manual concentration (Figure 4-2), and the agarose gel electrophoresis effect shows that the two methods of extract product fragments are distributed uniformly (Figure 4-3), and the nucleic acid quality for downstream applications (such as using Agilent Bioanalyzer system for DNA analysis, and qPCR and RT-PCR analysis) is basically consistent (Figure 4-4, 4-5). And in terms of operation, Leap-Pure S24 fully automatic nucleic acid extractor only needs to put the sample into the cartridge, which reduces manual operation time by more than 90% compared to manual extraction.

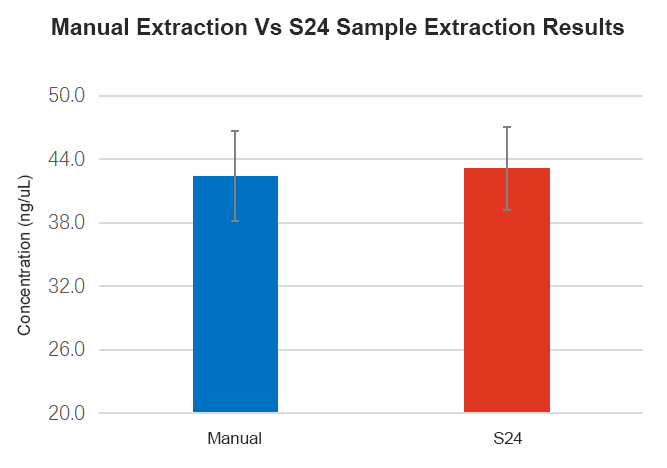
Figure 4-1 Comparison of Efficiency between Fully Automatic Nucleic Acid Extraction and Manual Extraction
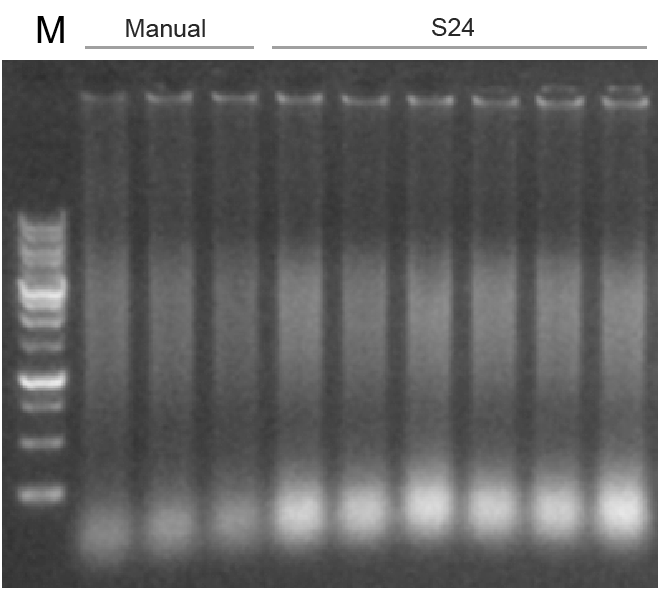
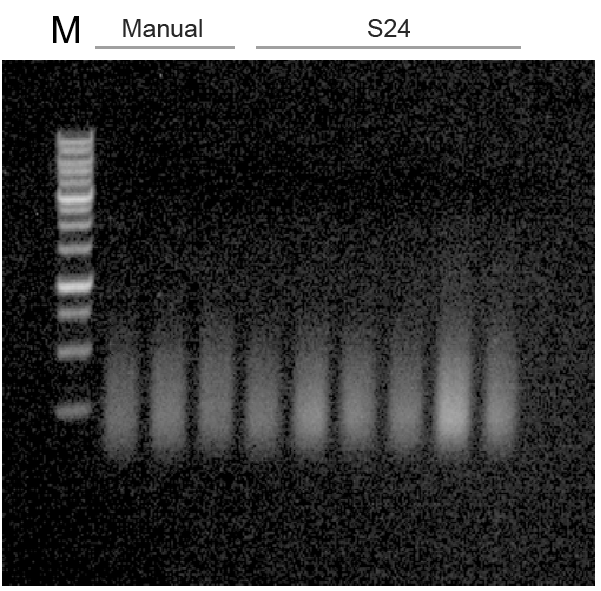
Figure 4-2 Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Results of Manual and S24 Extraction
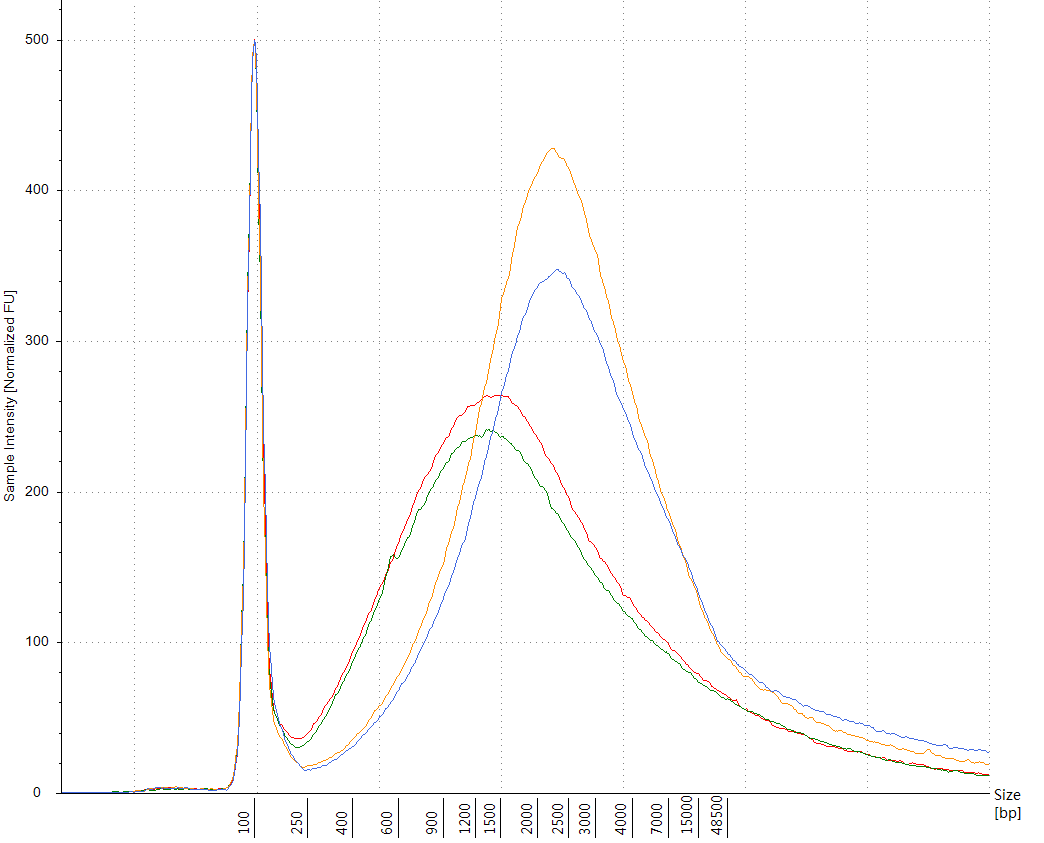
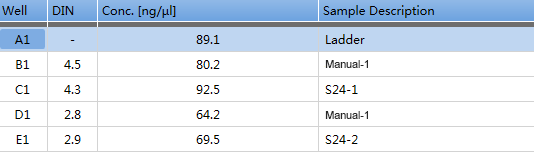
Figure 4-3 Fragment Analysis Results of Manual Method and S24 Extraction Product on Agilent 4150
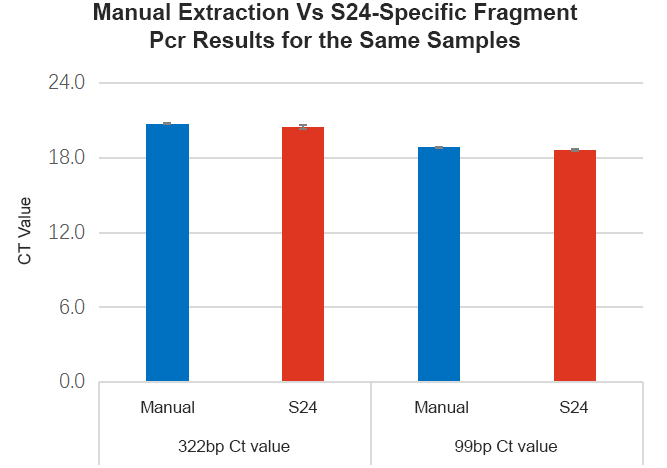
Figure 4-4 qPCR Results of S24 and Manually Extracted Products on Amplicons of Different Sizes
Summary
FFPE tissue samples are currently the most widely used form of tissue preservation at home and abroad. At present, molecular targeted therapy has gradually become the mainstream of tumor treatment. Detecting the gene mutation status of patients before clinical drug administration can correctly guide clinical individualized drug administration. Reduce the economic burden of patients and improve the therapeutic effect of molecularly targeted drugs. Therefore, the extraction of high-quality DNA from FFPE for molecular targeting detection has also gradually attracted attention. The DNA extracted from FFPE tissue samples that can be effectively amplified is not only suitable for retrospective studies, but also important for the diagnosis and identification of diseases, assessment of disease prognosis and exploration of disease molecular mechanisms.
Allsheng® FFPE tissue sample DNA extraction cartridges use efficient tissue lysis buffer and non-toxic dewaxing agent for one-step dewaxing and lysis. Using the principle of silica hydroxy magnetic beads and nucleic acid separation and purification methods, DNA is quickly and efficiently extracted from fixed solution tissues such as paraffin embedded tissue slices, paraffin blocks, or formalin. The concentration, fragment distribution, and quality (downstream experiments) of the DNA are consistent with the reference reagent. The reagent does not contain harmful substances such as xylene, and is easy to operate without the need for multiple centrifugations. This cartridge is suitable for various types of FFPE tissues and can be manually extracted or fully automated with supporting instruments. Paired with Leap-Pure S24 fully automated nucleic acid extractor, the extraction process can be fully automated, greatly reducing manual operation steps.

 Biological Sample Preparation
Biological Sample Preparation
 Life Science Detection Products
Life Science Detection Products
 POCT Detection & Reagent
POCT Detection & Reagent
 Automation & Liquid Handling
Automation & Liquid Handling
 Laboratory Instrument
Laboratory Instrument
 Reagent & Consumable
Reagent & Consumable
 Others
Others
 OEM/ODM
OEM/ODM












 Release time:2024-04-30
Release time:2024-04-30
 Source:
Source:
 Pageviews:1679
Pageviews:1679

























 + 86 571-88859758
+ 86 571-88859758 sales@allsheng.com
sales@allsheng.com



