mNGS-A Tool for Preventing Epidemics of Infectious Diseases After Natural Disasters
At 12:52 on September 5, 2022, an earthquake of magnitude 6.8 occurred in Luding County, Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan Province. So far, 93 people have died and more than 400 injured. After the earthquake disaster, it is easy to cause a series of disasters such as landslides, debris flows, and dammed lake bursts.
At present, Pakistan is suffering from a catastrophic flood disaster once in decades. Since mid-June, the floods in Pakistan have intensified and escalated. As of early September, 1.2 million houses have been engulfed, 5,000 kilometers of roads and 240 bridges have been destroyed, and 33 million people have been destroyed. People were affected and more than 1,200 people lost their lives.
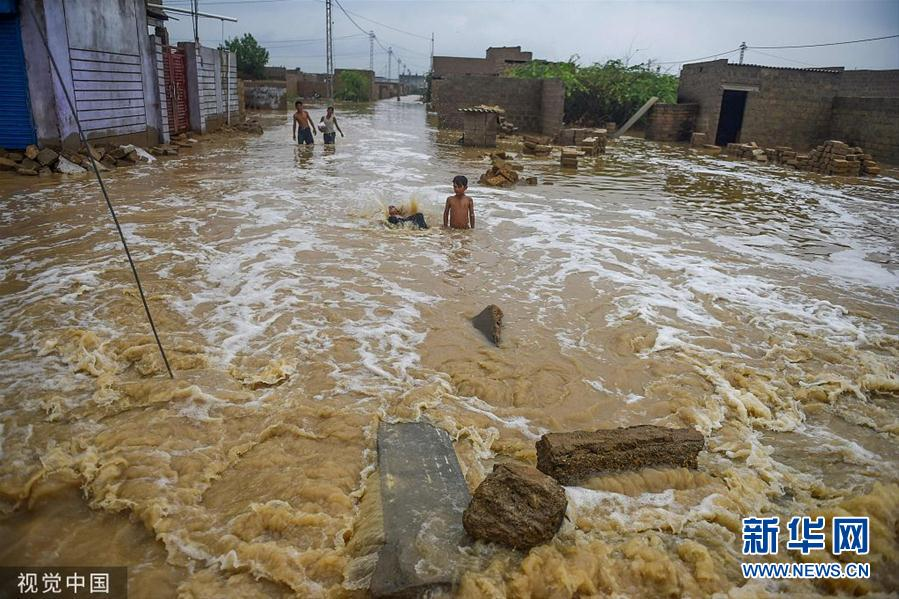

Source: Visual China
Disasters are often followed by the occurrence of various diseases, mainly infectious diseases. The ancients said: "After a major disaster, there must be a major epidemic." Natural disasters themselves will not lead to the occurrence of infectious diseases, but changes in water sources, food, living environment and other conditions often provide a hotbed for the spread of infectious diseases. Mainly in the digestive system and respiratory system infectious diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites and other pathogens. The following picture shows the infectious diseases that have been prevalent in many countries after natural disasters in the past 20 years:
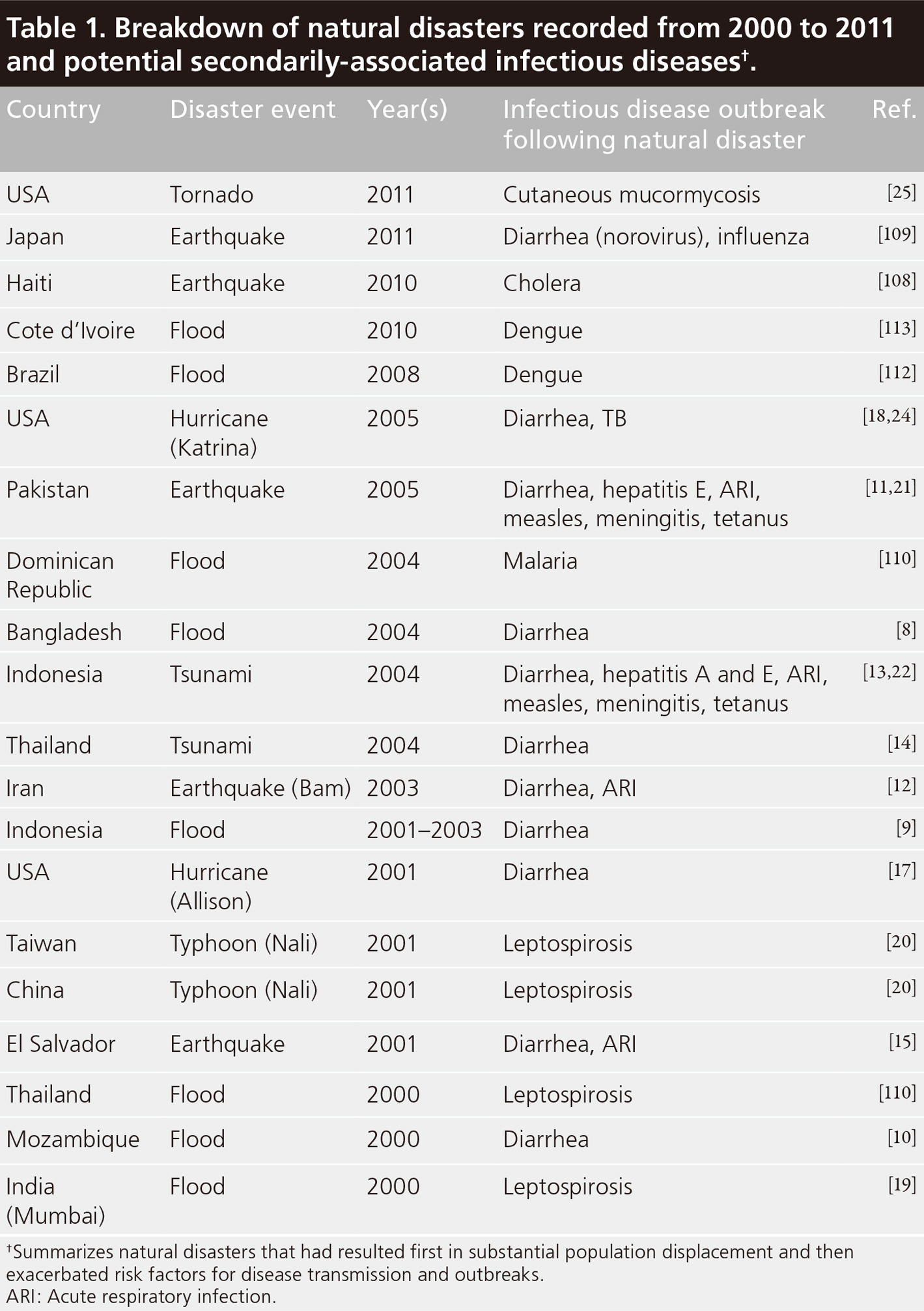
Source: Infectious diseases following natural disasters: prevention and control measures
In the event of a disease outbreak after a natural disaster, it is particularly important to be able to identify the cause and quickly diagnose it, which is an effective means to avoid the spread of the disease. NGS technology has shown great advantages at this time. Whether it is the diagnosis of the new coronavirus in early 2020, the African monkeypox virus that broke out in Europe and the United States this year, or the Legionella pneumonia currently prevalent in Argentina, genome sequencing is indispensable for diagnosis.
Metagenome sequencing (mNGS) is generally used in the diagnosis of emerging infectious diseases and infectious diseases with negative routine tests. Its screening for pathogens is not limited to infectious diseases, but covers the entire range of infectious diseases (infectious diseases include infectious diseases and other non-infectious pathogen-infected diseases). The detection of infectious diseases focuses on the detection rate, timeliness, functional index analysis, and rapid qualitative analysis of unknown pathogens. Traditional detection methods have the shortcomings of long pathogen culture cycles, low success rates, insufficient functional index analysis capabilities, and difficulty in achieving broad coverage. And gene sequencing provides a new way to solve these problems. mNGS will detect all microorganisms in the sample, rather than a single target like PCR, and does not need to know the sequence information of the pathogen to be tested in advance.
In genome sequencing technology, the most tedious operation is library preparation, which requires repeated addition of various reagents and waste liquids, but the quality of the library plays a decisive role in the sequencing results.
ALLSHENG Auto-NGS 100R is a fully automatic library preparation system, which can meet the simultaneous construction of 24 sample libraries at one time. It only needs to put in the prepared nucleic acid, and the library product can be obtained in a short time. Auto-NGS 100R not only improves the construction efficiency, but also guarantees the accuracy of samples and batch stability, and the operation software is graphically designed with clear operation logic, which greatly reduces the difficulty of use.


 Biological Sample Preparation
Biological Sample Preparation
 Life Science Detection Products
Life Science Detection Products
 POCT Detection & Reagent
POCT Detection & Reagent
 Automation & Liquid Handling
Automation & Liquid Handling
 Laboratory Instrument
Laboratory Instrument
 Reagent & Consumable
Reagent & Consumable
 Others
Others
 OEM/ODM
OEM/ODM












 Release time:2022-09-23
Release time:2022-09-23
 Source:
Source:
 Pageviews:3352
Pageviews:3352












 + 86 571-88859758
+ 86 571-88859758 sales@allsheng.com
sales@allsheng.com



