March 18, 2023 is the 23rd national protect liver day in China, with the theme of "active detection, expanded treatment, and elimination of hepatitis b hazards". The incidence of liver cancer is increasing year by year, posing a serious threat to people's health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates, there were about 906,000 new cases of liver cancer worldwide in 2020, with China accounting for about 45.3%. In China, liver cancer ranks as the 5th most common malignant tumor and the 2nd leading cause of cancer death. Most Chinese liver cancer patients have a history of hepatitis B virus infection/cirrhosis, and most of them are already in the middle and late stages (70%) at the time of diagnosis. In addition, liver cancer in the Chinese population has a low survival rate. A 17-item statistical analysis of the survival rate of Chinese cancer patients published in the Lancet-Global Health showed that the 5-year survival rate of Chinese liver cancer patients was only 12.1%.
Limitations of Common Detection Methods
The occurrence of liver cancer is the result of the synergistic effect of multiple factors, the involvement of multiple oncogenes and related genes, and the mutation of multiple genes. According to available information, the main causative factors of liver cancer include hepatitis virus, aflatoxin, alcoholic liver disease and metabolism-related fatty liver disease, drinking water pollution, alcohol consumption, genetics and other factors (including malnutrition, etc.).
At present, the traditional clinical diagnosis of liver cancer in China mainly relies on the three major techniques of serology, imaging and pathology, among which serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and liver ultrasound are the main means of early screening of liver cancer. The sensitivity of ultrasonography for the diagnosis of liver cancer less than 2 cm is only 30%, and it cannot distinguish between benign and malignant tumors; the sensitivity of AFP test is only about 40-60%, and the diagnostic level for early liver cancer is only 30%-40%, therefore, the existing technology is far from meeting the demand for early diagnosis of liver cancer.
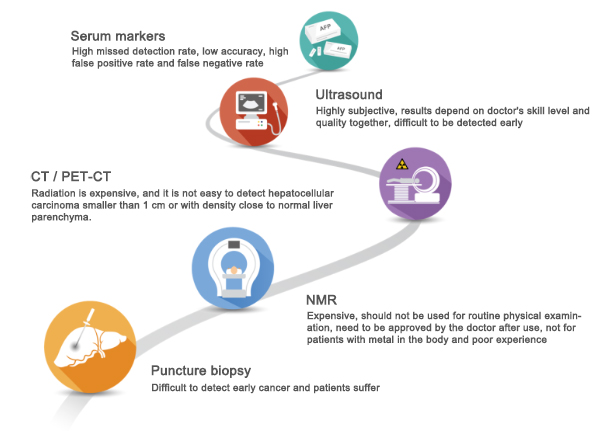
Figure 1 Common Technical Methods and Limitations of Early Screening for Liver Cancer
Advantages of ctDNA Non-invasive Methylation Testing Technology
In recent years, with the rapid development of genetic testing technology, scientists can detect trace amounts of tumor nucleic acid characteristics in the blood circulation for early diagnosis of tumors, a method called liquid biopsy technology, which is a quantum leap from traditional invasive tissue biopsy. The main biomarkers of liquid biopsy include circulating tumor cells (CTCs), circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), cell free DNA (cfDNA), exosome, microRNA and methylated DNA.
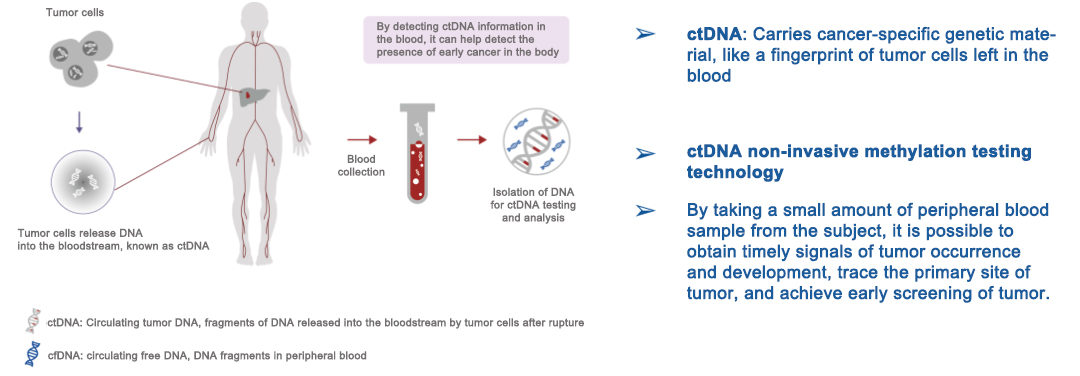
Figure 2 Significance of ctDNA Detection in Liquid Biopsies
DNA methylation alterations, especially those of the oncogene CpG island, play an important role in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). A number of studies have shown that methylation abnormalities of various genes are more effective than AFP in the diagnosis of HCC. Xu et al. developed a diagnostic model for HCC based on 10 methylation genes by measuring the methylation levels of specific sites in peripheral blood ctDNA of HCC patients and healthy controls, and its sensitivity and specificity for detecting HCC in the validation set were 83.3% and 90.5%, respectively, with an AUC of 0.944. Another diagnostic model consisting of six aberrant methylation genes, including HOXA1, EMX1, ECE1, Another diagnostic model consisting of six aberrantly methylated genes, including HOXA1, EMX1, ECE1, AK055957, PFKP, and CLEC11A, was validated in different clinical cohorts over multiple phases and was shown to be highly effective in the diagnosis of HCC: sensitivity of 95%, specificity of 92%, and AUC of 0.96. In addition, the 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) assay has also been reported to have good performance in the diagnosis of early HCC. Cai et al. developed and validated an HCC diagnostic model based on cfDNA genome-wide 5-hmC assay data with an AUC of 0.85 for differentiating chronic liver disease from early HCC, which was significantly better than that of AFP (AUC 0.69).
Allsheng provides universal solutions for early tumor screening based on its three self-developed technology platforms.
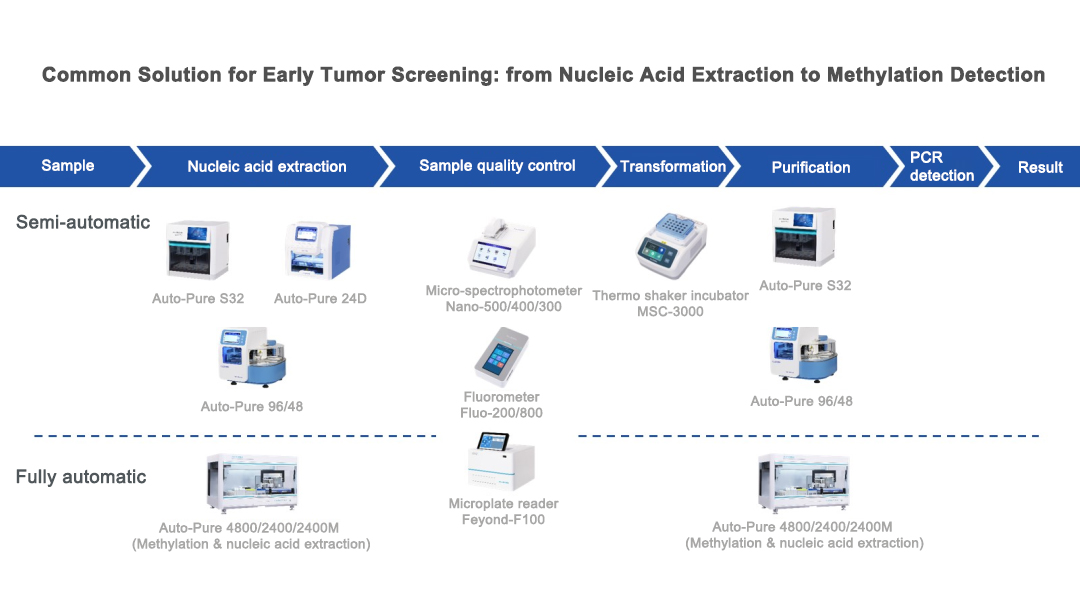
Reference
[1] China Anti-Cancer Association Liver Cancer Committee. Chinese Guidelines for Integrated Cancer Diagnosis and Treatment (CACA)-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Section[J]. Electronic Journal of Comprehensive Cancer Therapy, 2022, 8(3): 31-63.
[2] Medical Administration of the National Health Care Commission of the People's Republic of China. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer (2022 edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Liver Diseases, 2022, 30(4): 367-388.
[3] He J, Chen WQ, Shen HB, et al. Guidelines for liver cancer screening in Chinese population (2022, Beijing) [J]. Journal of Clinical Hepatobiliary Diseases, 2022, 38(8): 1739-1758
[4] Xu RH,Wei W,Krawczyk M,et al. Circulating tumour DNA methylation markers for diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma [J]. Nat Mater,2017,16(11): 1155-1161.
[5] Kisiel JB,Dukek BA,V S R Kanipakam R,et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Detection by Plasma Methylated DNA:Discovery,Phase Ⅰ Pilot,and Phase Ⅱ Clinical Validation [J]. Hepatology,2019,69(3):1180-1192.[12] Cai J,Chen L,Zhang Z,et al. Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosines in circulating cell-free DNA as a non-invasive
approach for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma [J].Gut,2019,68
[6] 2195-2205.[13]Cohen JD,Li L,Wang Y,et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test [J].Science,2018,359(6378):926-930.
[7] Qu C,Wang Y,Wang P,et al. Detection of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma in asymptomatic HBsAg-seropositive individuals by liquid biopsy [J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A,2019,116(13): 6308-6312.[15] Zhang X,Wang Z,Tang W,et al. Ultrasensitive and affordable assay for early detection of primary liver cancer using plasma cell-free DNA fragmentomics [J].Hepatology,2022,76(2):317-329.
[8] Chen L,Abou-Alfa GK,Zheng B,et al. Genome-scale profiling of circulating cell-free DNA signatures for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients [J].Cell Res,2021,31(5):589-592.

 Biological Sample Preparation
Biological Sample Preparation
 Life Science Detection Products
Life Science Detection Products
 POCT Detection & Reagent
POCT Detection & Reagent
 Automation & Liquid Handling
Automation & Liquid Handling
 Laboratory Instrument
Laboratory Instrument
 Reagent & Consumable
Reagent & Consumable
 Others
Others
 OEM/ODM
OEM/ODM












 Release time:2023-03-18
Release time:2023-03-18
 Source:
Source:
 Pageviews:3432
Pageviews:3432












 + 86 571-88859758
+ 86 571-88859758 sales@allsheng.com
sales@allsheng.com



